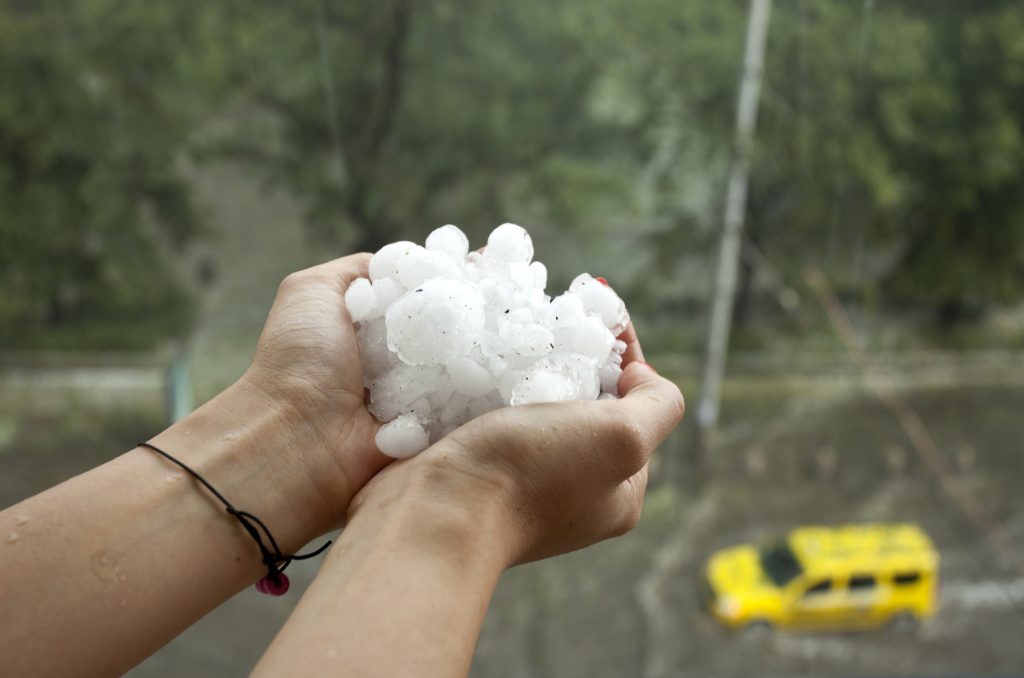
Hailstones are one of nature’s most fascinating and destructive weather phenomena. They form high in the atmosphere during severe thunderstorms, growing layer by layer as they are repeatedly carried into freezing temperatures. Understanding how hailstones develop, their structure, and their impact can shed light on the power of storms and the devastation they can cause.
How Hailstones Form
Hail begins as tiny water droplets in a thunderstorm. The process unfolds within towering storm clouds, where temperatures plunge below freezing, and powerful updrafts keep water and ice particles suspended. Here’s a closer look at the formation process:
- Nucleation: Each hailstone starts with a nucleus—often a small particle of dust, pollen, or other debris. This nucleus provides a surface for supercooled water droplets to freeze upon.
- Updrafts: Strong storm updrafts lift the nascent hailstone higher into the cloud, where temperatures are colder. As the hailstone is carried upward, it collects more supercooled water, which freezes and adds layers of ice.
- Growth Cycles: The hailstone experiences multiple updraft and downdraft cycles, accumulating new layers of ice during each trip. This cyclical journey determines the size, shape, and composition of the hailstone.
The Growth Process: Layers of Ice
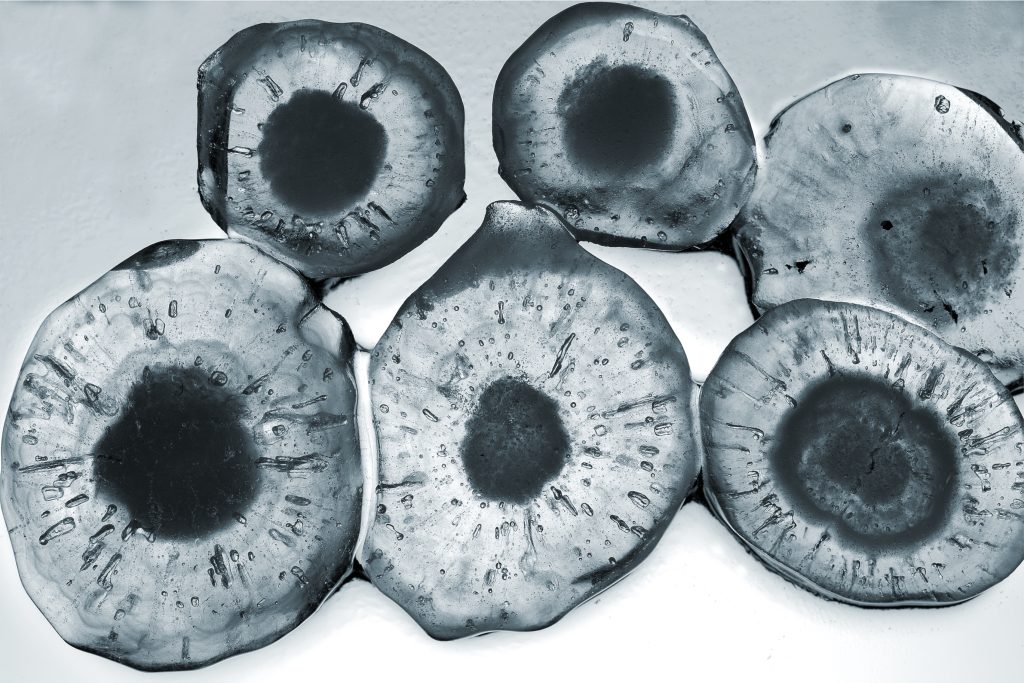
Hailstones grow in distinct layers of ice, each providing clues about the conditions within the storm.
- Dry Growth: When supercooled water freezes instantly upon contact with the hailstone, it forms cloudy, lightweight layers. These layers contain trapped air bubbles.
- Wet Growth: If the water doesn’t freeze immediately, it spreads out and solidifies more slowly, forming clear, dense layers of ice. Wet growth occurs when temperatures are slightly warmer but still below freezing.
The alternation between these growth modes results in a hailstone with a layered structure, much like the rings of a tree. Each layer represents a different phase of the storm’s lifecycle, providing valuable information for meteorologists.
Size and Shape: What Determines the Final Form
The size and shape of hailstones depend on various factors within the thunderstorm:
- Size: The strength of the updrafts determines how large a hailstone can grow. Stronger updrafts can keep hailstones suspended longer, allowing them to accumulate more layers of ice. Hailstones can range from pea-sized to softball-sized or larger.
- Shape: Hailstones are not always perfectly round. Collisions with other hailstones or melting during descent can create irregular shapes. These unique forms can influence how much damage a hailstone causes upon impact.
The Destructive Potential of Hailstones
Hailstones may appear innocuous at first glance, but their destructive power lies in their size, speed, and density.
- Size and Velocity: Larger hailstones fall faster due to their greater mass. A golf ball-sized hailstone, for instance, can reach speeds of up to 50-60 mph, delivering significant kinetic energy upon impact.
- Density: The dense, clear ice formed during wet growth is particularly damaging because it absorbs and transfers impact energy more effectively than lighter, cloudy ice.
Hailstones are responsible for billions of dollars in damage annually, affecting vehicles, buildings, crops, and even human safety.
Studying Hailstones: Unlocking Storm Secrets
Hailstones are more than just destructive ice chunks; they are also valuable tools for studying severe weather. By analyzing their layers, scientists can reconstruct the conditions within a storm and gain insights into its intensity and evolution. Modern radar technology also aids in detecting hail during storms, helping communities prepare and respond more effectively.
Record-Breaking Hailstones
Some hailstones reach extraordinary sizes, leaving a lasting impression on the communities they impact.
- World Records: The largest hailstone ever recorded fell in South Dakota in 2010, measuring over 8 inches in diameter and weighing nearly 2 pounds.
- Fascinating Finds: Hailstones occasionally encase debris, such as leaves, insects, or small twigs, offering a glimpse into the chaotic environment of a storm.
Preparing for Hailstorms
While hailstorms are unpredictable, you can take steps to minimize their impact:
- Protect Vehicles: Use covered parking or hail-resistant car covers to shield your vehicle.
- Reinforce Structures: Install impact-resistant roofing materials to safeguard your home.
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather alerts and seek shelter when severe storms are predicted.
Understanding Hail’s Impact
The anatomy of a hailstone reveals the dynamic processes within thunderstorms and highlights the immense power of nature. By understanding how hailstones form and grow, we can better appreciate their impact and take steps to mitigate their destructive effects. Whether you’re marveling at their layered structure or preparing for the next storm, hailstones serve as a reminder of nature’s complexity and force.



